Download PDF
Download page External u-blox GNSS.
External u-blox GNSS
Doc for Ellipse firmware < 3.0
You are currently viewing the documentation for an Ellipse running firmware version v2.x or earlier. If your Ellipse is operating on firmware version ≥ 3.0, please use the version picker in the top-right corner of the page to select the appropriate version.
This brief document guides you in the process of configuring an external Ublox GNSS receiver for your Ellipse INS products.
Use this document in complement of the Operating Handbooks.
Step 1: GNSS and Ellipse connections
Connect GNSS Tx signal(s) pin to the Rx pin on one of the following Ellipse connectors: PORT A, B, C, D or E. Please also connect Ellipse and GNSS ground signals to each other.
Connect GNSS PPS signal pin to Sync A, B, C or D input pin.
Step 2: GNSS module configuration
Basic operation
Configure the following outputs and output rates on your GNSS receiver:
- UBX-NAV-PVT @ 5 Hz
- UBX-NAV-HPPOSLLH @ 5 Hz
- UBX-NAV-SIG @ 1Hz
PPS signal
For proper operation, a PPS signal must be provided at 1 Hz.
Adding post-processing capability
The following additional message configuration is required for post-processing.
- UBX-RXM-RAWX @ 1Hz
Step 3: Ellipse configuration
In order to configure the Ellipse-E, you need to use the sbgCenter and open the configuration window. Simply follow those instructions:
Set aiding assignment
In this window, you just indicate where you connected your GNSS receiver.
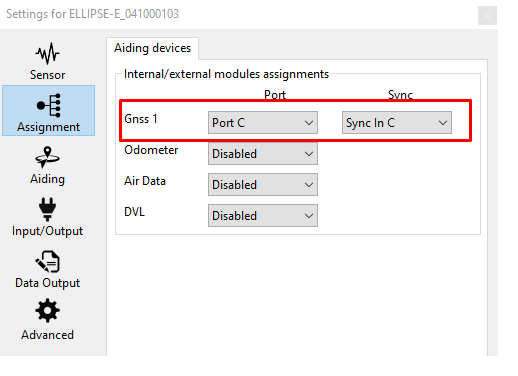
Both communication port and Sync In pin must be set.
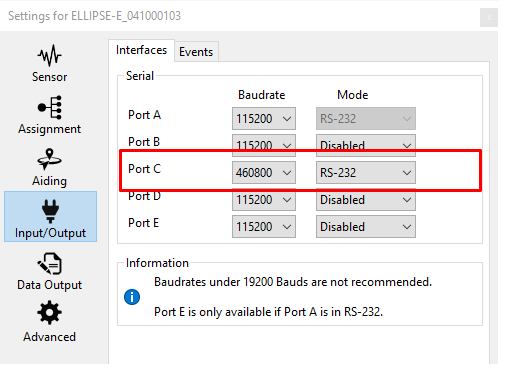
Set correct baud rate and mode for serial port
In our example we configured the GNSS to be connected on PORT C in RS‑232 mode using a baudrate of 460800 bauds.
Set logic input configuration for PPS signal
In order to use correctly PPS signal information, you must enable the corresponding logic input. Here we configured PPS on Sync C.
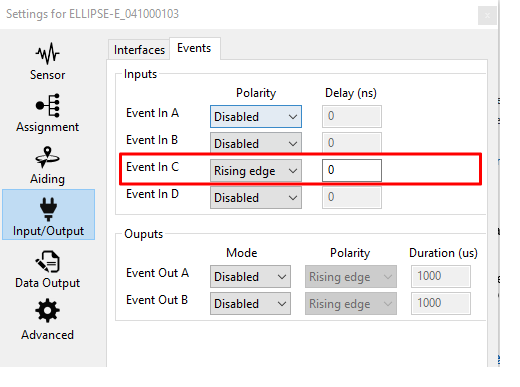
Polarity should be set accordingly with the actual PPS signal (rising edge or falling edge).
Set correct GNSS model and configuration
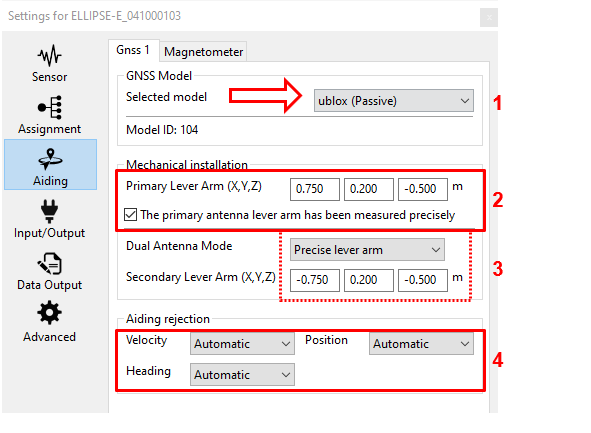
GNSS model should be set to Ublox (Passive).
GNSS lever arms are to be measured with 5 cm accuracy FROM the IMU TO the antenna phase center (APC), in the vehicle frame. If the option “The primary antenna lever arm has been measured precisely” is ticked, then the Extended Kalman filter will take these values for granted and will not estimate any values for this Primary antenna lever arm. It should help the system to align faster, but in this case, the Primary antenna lever arms must be measured within 1 cm accuracy.
In case of Dual antenna system, the secondary antenna lever arm must also be entered FROM the IMU TO the antenna phase center (APC), and the same accuracy requirements as for the primary antenna apply, depending if the above selection box is set to "Precise" or "Rough" lever arm value.
Finally, each available measurement (position, velocity, and heading if available i.e. if using a dual antenna receiver) should be configured to be used or not. Automatic is recommended.
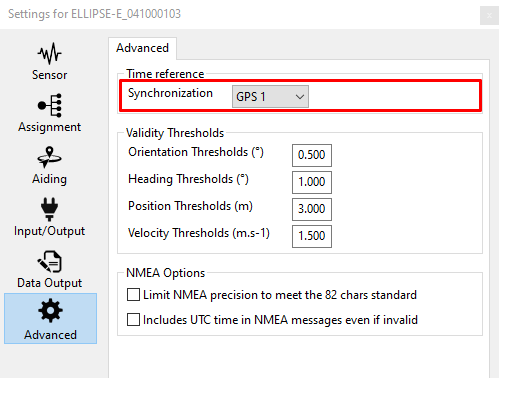
Check clock alignment
Finally, you check that the time synchronization reference is set to GPS 1 (default configuration).
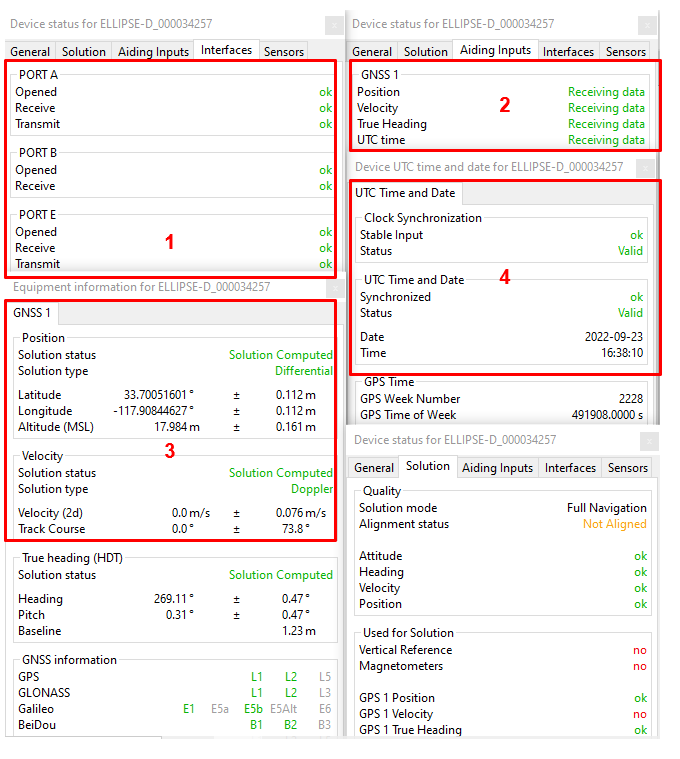
Step 4: Checking status
The status and GNSS windows should be checked carefully before going further. These status indicators will give essential hints in case of troubles to get a correct fix. Each step is labeled in red in the following screenshot.
Corresponding COM port must be OK.
GNSS 1 frame in “Aiding Inputs” tab must show that the data is received. Not seeing this would probably imply that there is a baudrate or wiring issue.
After that, you can check if the GNSS solution has been calculated and is consistent.
Then you can check the "Clock" section. Input clock must be OK and UTC time should be set to valid after a few minutes in steering mode.