Download PDF
Download page External Trimble GNSS integration.
External Trimble GNSS integration
This brief document guides you in the process of connecting an external Trimble GNSS receiver to your SBG High Performance products.
Use this document in complement of the “Operations” Operating Handbooks.
Step 1 : GNSS and sensor connections
Two physical communication layers can be used for feeding the aiding data frames to the INS : serial communications (recommanded) or Ethernet (not in the scope of that document).
In both case, connect GNSS PPS signal to an available Sync Input.
In case of serial communications, connect GNSS Tx signal(s) to one of the available serial ports Rx pin.
Step 2 : GNSS module configuration
Basic operation
Configure the following outputs in GSOF format and output rates on your GNSS receiver:
- Lat, Long, Ht @ 5 Hz
- Position Sigma @ 5 Hz
- Position time @ 5 Hz
- Position Type Information @ 5 Hz (optional)
- Velocity @ 5Hz
- Current Time UTC @ 1Hz
- Detail All SV @ 1Hz
- Attitude Info @ 5 Hz (for dual antenna systems)
Some Trimble GNSS can't output the Position Type Information message. However, this message is not mandatory for correct INS operations.
If your receiver doesn't support the Detail All SV message log, you can use the Brief All SV Info or the Multiple Page Detail All SV one.
Adding post-processing capability
Post processing requires getting RAW measurement data from the GNSS receiver. Trimble GNSS receivers use the RT-17 or RT-27 protocols to do so. The RT-27 protocol support all constellations whereas the RT-17 is a deprecated protocol only supporting the GPS system.
The following RT-17/27 configuration should be set on the Trimble GNSS for correct post processing operations:
- Epoch Interval : Measurements / Positions @ 1Hz
- Concise : enabled
- R-T Flag : enabled
- Send Raw GPS Data : enabled
- Multi-System Support : enabled
- Include Doppler : enabled
- GPS Ephemeris, GLONASS Ephemeris, QZSS Ephemeris : When new one is available
Please select a sufficient baud rate to transfer all enabled data. If post processing (RT-17/27) outputs are enabled, we recommend using 460 800.
Other GNSS Configuration
General Configuration:
- 1PPS On/Off : Enable
- 1PPS Always On : Disable
Position Configuration :
- PDOP Mask : 20
- RTK Mode : Low Latency
- Autonomous Engine : Kalman
- Motion : Kinematic
- Signal Tracking bandwidth : Wide
Tracking Configuration:
- Elevation Mask : 10
- Everest : Enable
- Clock Steering : Enable
Step 3 : Sensor configuration
In order to configure the Sensor, you need to connect to the Web interface and open the configuration window. Simply follow those instructions:
Set aiding assignment
In this window, you just indicate where you connected your GNSS receiver.
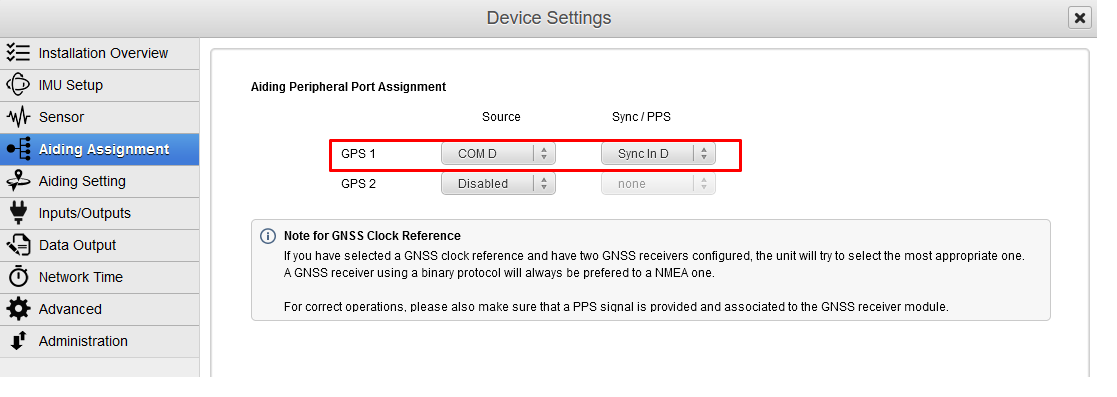
Both communication port and Sync In pin must be set.
If you have two connected GNSS receivers, only the primary GNSS receiver should provide a PPS source to accurately time stamp the data.
Set correct baudrate and mode for serial port
In our example we configured the GNSS to be connected on PORT D in RS‑232 mode using a baudrate of 460800 bauds.
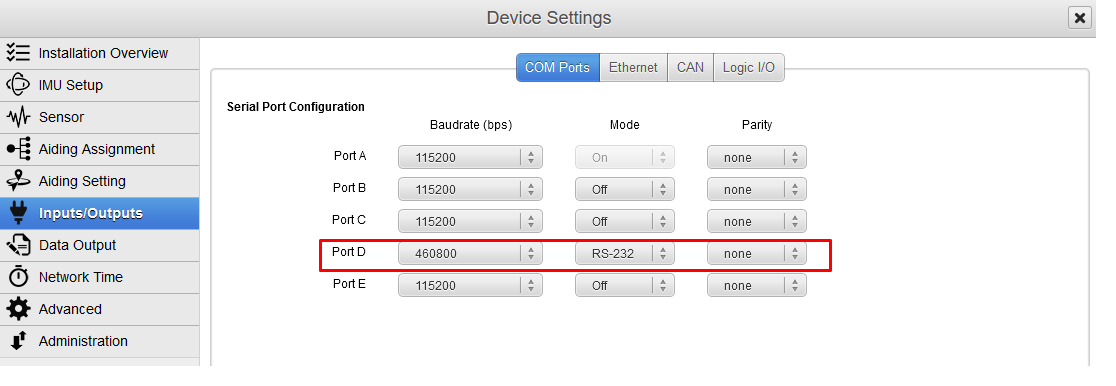
Post Processing messages contain a lot of packets, sufficient baudrate speed should be then selected. We recommend a speed of 460800 bauds in that case.
Set logic input configuration for PPS signal
In order to use correctly PPS signal information, you must enable the corresponding logic input. Here we configured PPS on Sync In D.
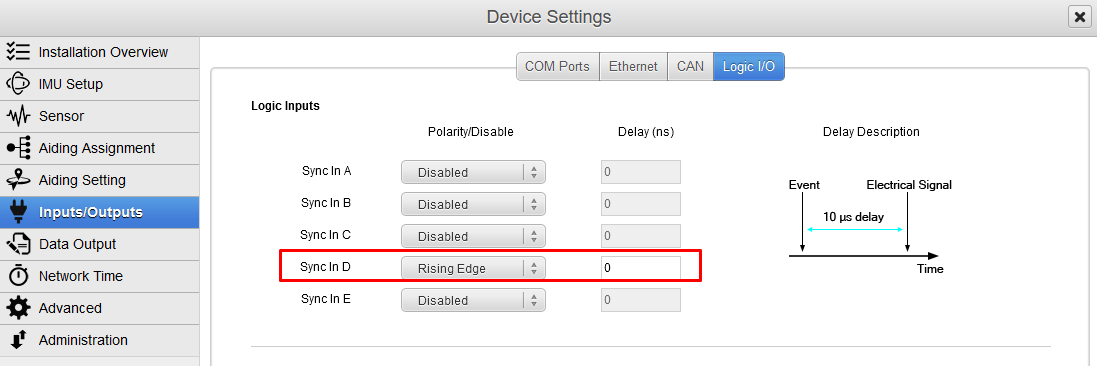
Polarity should be set accordingly with the actual PPS signal which is provided by your GNSS receiver.
Set correct GNSS model and configuration
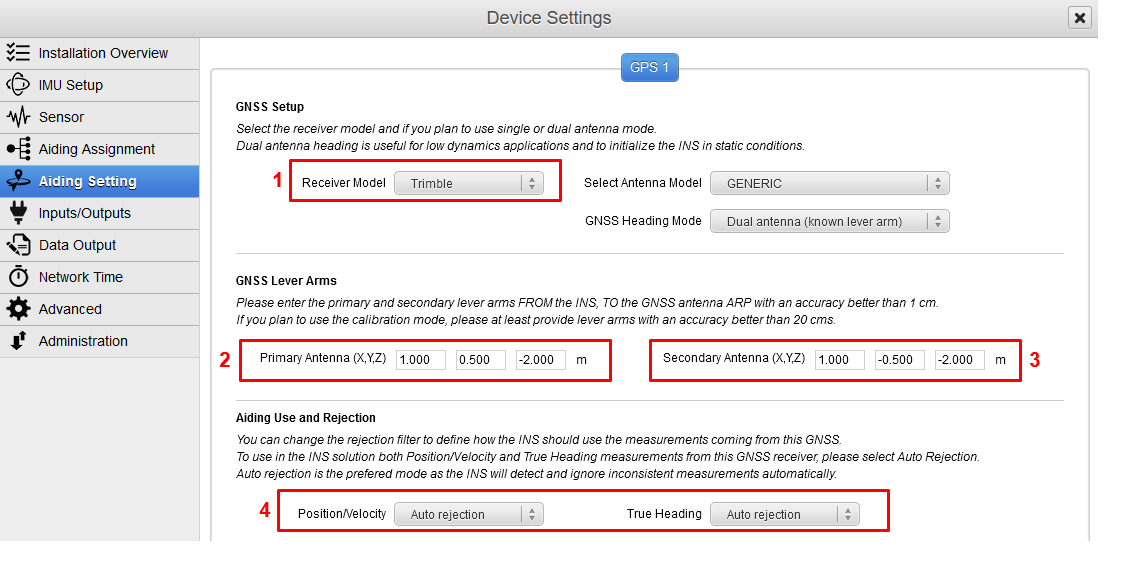
GNSS model should be set to Trimble.
GNSS Primary lever arm has to be entered within a 1 cm accuracy FROM the IMU reference point, TO the antenna reference point (ARP), in the vehicle frame.
In Dual Antenna (known lever arm) mode, offset for the secondary antenna (providing heading) must also be entered, FROM the IMU reference point, TO each antenna reference point. It is also possible to select Dual Antenna (auto lever arm) if a calibration is planned for the antennas lever arms.
Finally, each available measurement (position/velocity and true heading if available) should be configured to be used or not. Auto rejection mode is recommended.
In order to increase the precision of the measurements it is recommended to select the actual Antenna model from the droplist. If you don't know what model to choose, you can select "Generic". In that case, the measured lever arms should refer to your antenna phase center (APC).
When using an external GNSS receiver, it is highly recommended to have the same antenna model selected on the GNSS receiver and the INS settings.
If you cannot measure the lever arms to 1 cm accuracy, a calibration can be performed. See Lever Arms Calibration Procedure.
Step 4 : Checking status
Once fully configured, the global status must be checked :
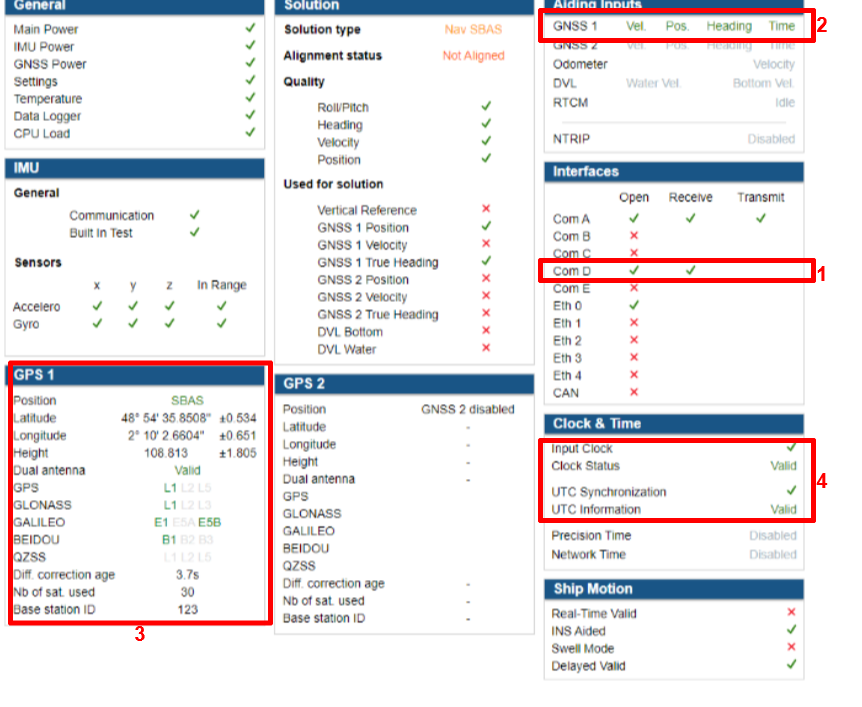
- Corresponding COM port must be opened and Rx flag OK. Baudrate should be the same in the GNSS and the SBG unit configuration.
- GNSS 1 or 2 line in “Aiding Inputs” section must show valid data.
- GNSS solution is reported in that section. Check if there is a good GNSS fix here.
- Then you can check at the Clock section. Input clock must be OK and UTC time should be set to valid after a few minutes in alignment mode.