In this article we'll learn how to output data to other systems via various ports. Each port (once enabled) will show a tab in Data output so you can fine tune the data and its rate on each port.
Ethernet Ports
In Inputs/Outputs COM Ethernet tab:
In this example your INS is configured in Static IP mode, in the IP range 192.168.137.0/24 .The subnet mask being 255.255.255.0, it mean all IP's between 192.168.137.0 to 192.168.137.255.
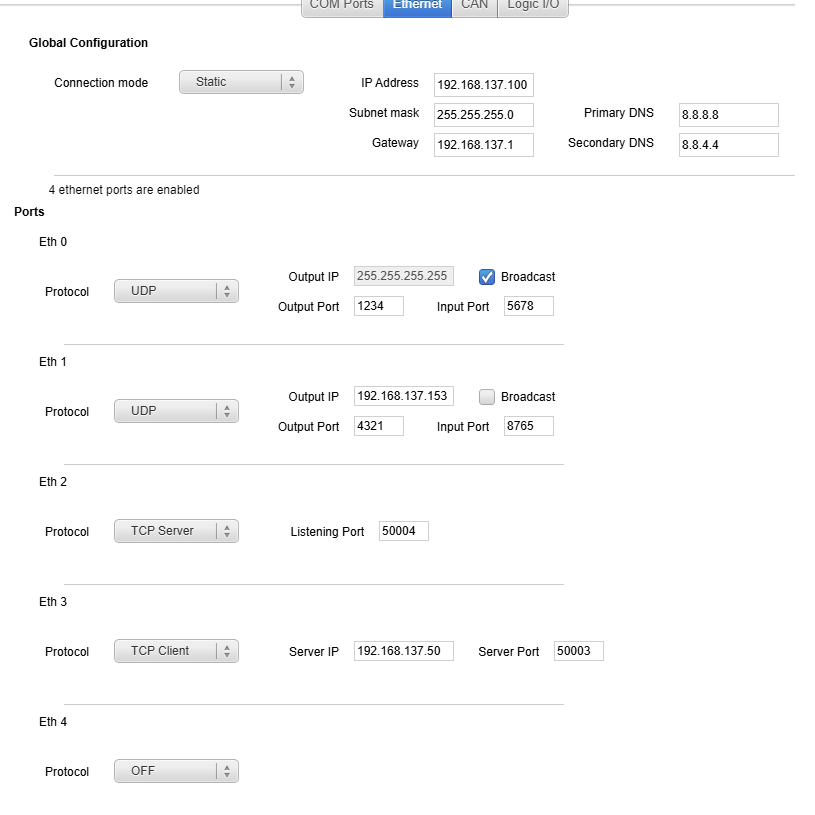
The HPI has a UNIQUE IP 192.168.137.100, and 4 ETH ports are opened now (up to 5). Note that the input/output ports are different for each ETH ports. This is important even on UDP.
ETH-0 in UDP 'broadcast' will broadcast to any IP within the range 192.168.137.0/24. on port 1234, and listen (from any IP) on port 5678.
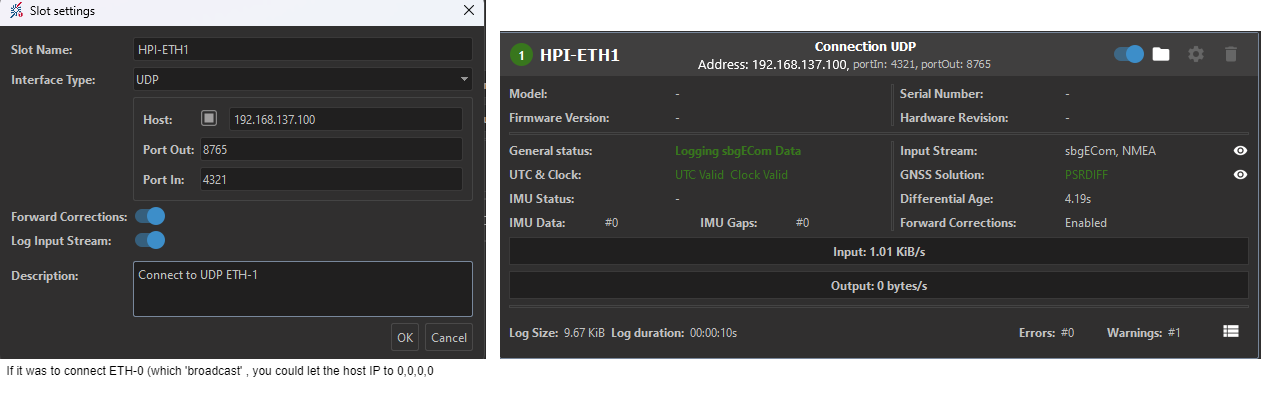
ETH-1 in UDP will broadcast only to the Output IP (target IP) 192.168.137.153 on port 4321, and listen only from 192.168.137.153 on port 8765.
ETH-2 in TCP-Server will transmit data on port 50004, the other system will then connect to HPI INS to listen from 192.168.137.100:50004
ETH-3 in TCP-Client will listen for data from the server IP 192.168.137.50:50003 (could be for exemple some RTCM corrections from a base)
When setting up a system to receive UDP traffic, Like sbgDataLogger, the input port of that system is the output port from INS, and the output port of that system is the input port from INS.
Serial Ports
In Inputs/Outputs COM Ports tab, simply enable the serial port to either RS-232 or RS-422, and setup the baud rate and parity.
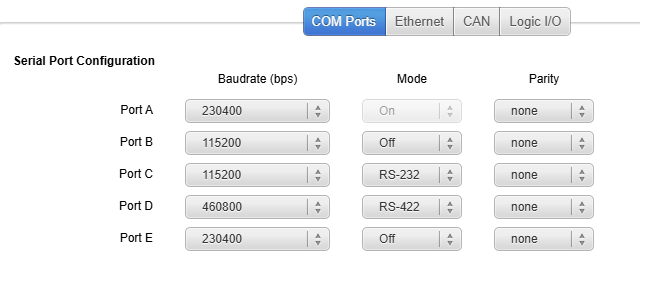
Only port-A is automatically detecting the mode of connection (is always on)
Depending on the cable you are using, you may have to connect a null/modem between your port and the other systems serial port.
Data Outputs configuration
In Data Output, for each visible tab, selection the data and its rate is thoroughly described in the page Data-Logging For Support Purpose.